Asphalt pavement is one of the most widely used surface materials in the world. To understand the purpose of asphalt sealcoating, it helps to know how asphalt pavement originated, what it is made of and why it needs ongoing maintenance.
What You’ll Learn
- A Brief History of Asphalt Pavement
- What Asphalt Pavement Is
- How Asphalt Pavement Is Built
- Why Asphalt Pavement Fails
- What Sealcoating Does for Asphalt Pavement
- Benefits of Asphalt Sealcoating
- How Asphalt Sealcoating Protects Pavement
- How to Apply Asphalt Sealcoating
- How Often to Sealcoat Pavement
- Learn More About How to Sealcoat
- SealMaster Expertise & Support
A Brief History of Asphalt Pavement
Asphalt has been used for road construction for thousands of years.
- The first road paved with asphalt was built in Babylon between 625 and 604 B.C.
- In the United States, the first asphalt road was paved in 1870 in Newark, New Jersey, by Belgian chemist Edmund J. DeSmedt.
- Asphalt paving grew rapidly in the early 1900s due to expanded oil refining and the rise of the automobile.
Today, the United States has nearly 4 million miles of paved roads and billions of square feet of asphalt pavement, parking lots and driveways.

What Asphalt Pavement Is
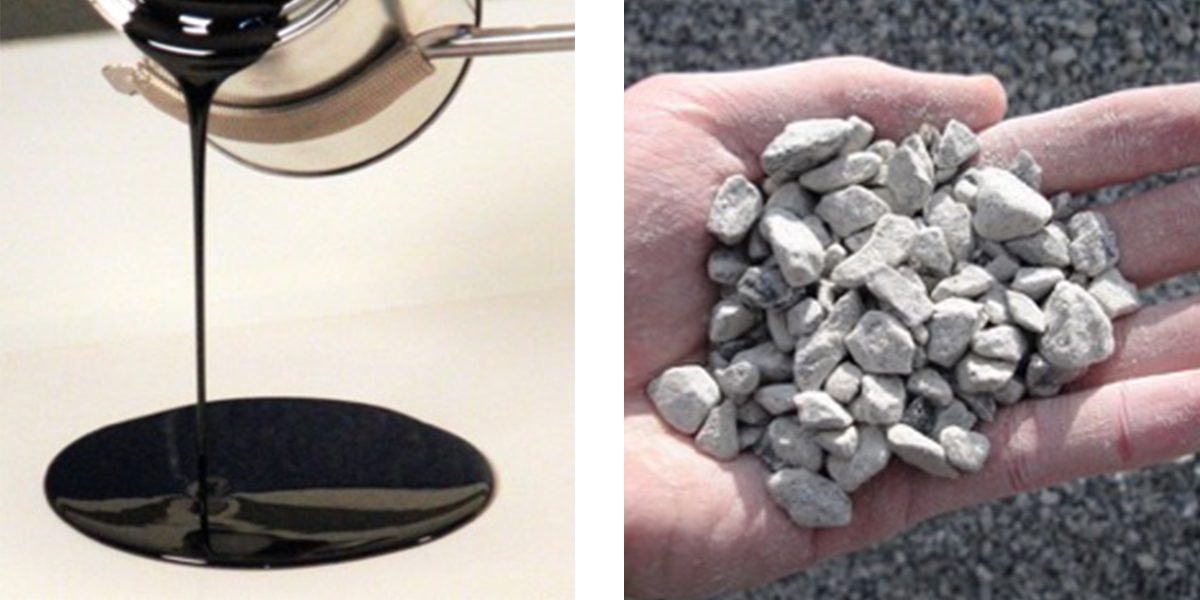
Asphalt pavement is composed of heated liquid asphalt cement and specifically graded crushed rock.
- Liquid asphalt, also called asphalt cement, is a byproduct of the oil refining process.
- It is the dark, viscous material left after gasoline, solvents and other light-end products are distilled from crude oil.
In simple terms, asphalt pavement consists of:
- Stone, rock or gravel (aggregate)
- A binder called asphalt cement that holds the aggregate together
Maintaining the strength of this binder is essential to preserving the pavement.

How Asphalt Pavement Is Built
Hot-mix asphalt pavement is produced in an asphalt plant and transported by truck to the construction site. Installation follows a structured process:
- A layer of crushed stone is placed over a prepared, compacted soil sub-base.
- Hot-mix asphalt is placed over the stone using an asphalt laydown machine.
- The asphalt mat is rolled and compacted while still hot.
Proper base preparation and compaction are critical to pavement performance.

Why Asphalt Pavement Fails
Asphalt begins to deteriorate as soon as it is exposed to the environment.
Environmental factors include:
- Moisture
- Oxidation
- Freeze-thaw cycles
- Chemicals
Traffic loading also places stress on pavement, accelerating deterioration.
Quality issues during paving may include:
- Poor-quality mix
- Hot mix that cooled before placement
- Application that was too thin
- Inadequate base preparation
Over time, rain, UV rays and chemicals attack the binder in asphalt pavement. As the binder weakens, the pavement becomes brittle, leading to cracks and surface failure.
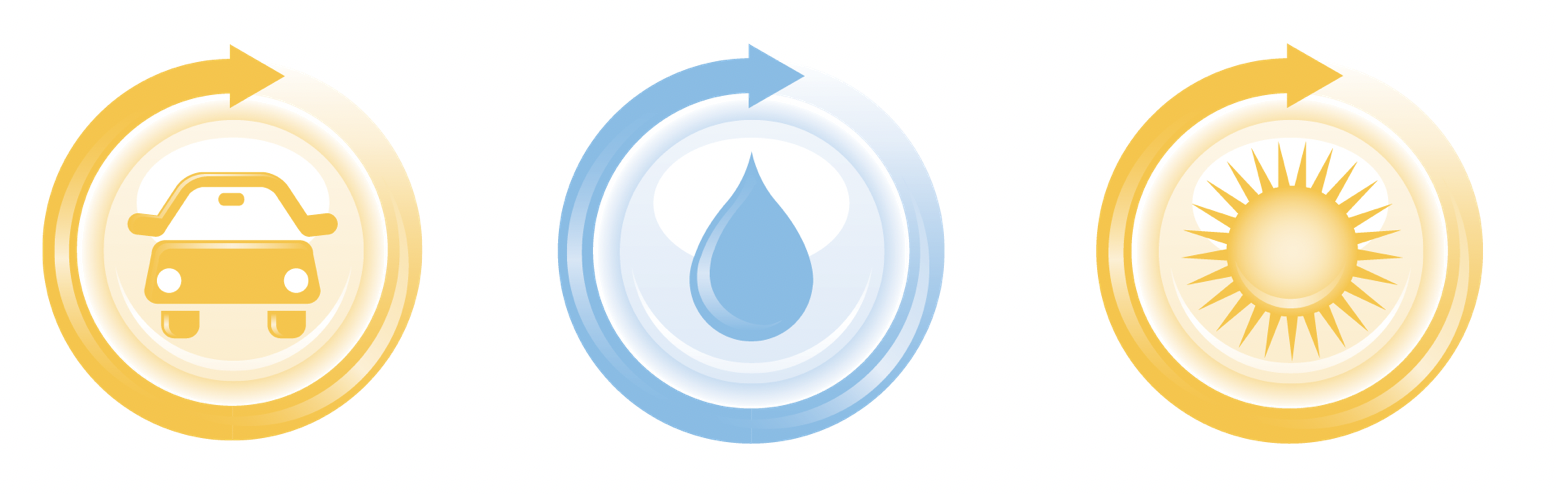

What Sealcoating Does for Asphalt Pavement
While asphalt sealcoating refers to the process of protecting and preserving asphalt pavement, sealer is the material used to perform that work. Sealer is formulated as a protective coating designed to bond to the surface of asphalt and shield it from water, oils, UV rays and chemical exposure. A high-quality sealer helps restore the pavement’s appearance, slows oxidation and provides the flexible, durable finish that allows asphalt surfaces to last longer. Using the right sealer is essential to achieving consistent performance and long-term pavement protection.
Asphalt Sealcoating:
- Replenishes binder lost through weathering and aging
- Blocks moisture, oils and UV damage
- Restores a deep black finish that enhances curb appeal
Asphalt Sealer is typically a bituminous- or acrylic-based liquid that includes:
- Water
- Silica sand
- Polymer additives
- Proprietary fillers and solids
It can be applied by brush, spray or squeegee.
Benefits of Asphalt Sealcoating
Sealcoating provides multiple performance, aesthetic and financial benefits.
Protection
- Helps safeguard the binder in asphalt pavement
- Reduces the impact of moisture, oxidation and chemicals
- Helps prevent brittleness and cracking
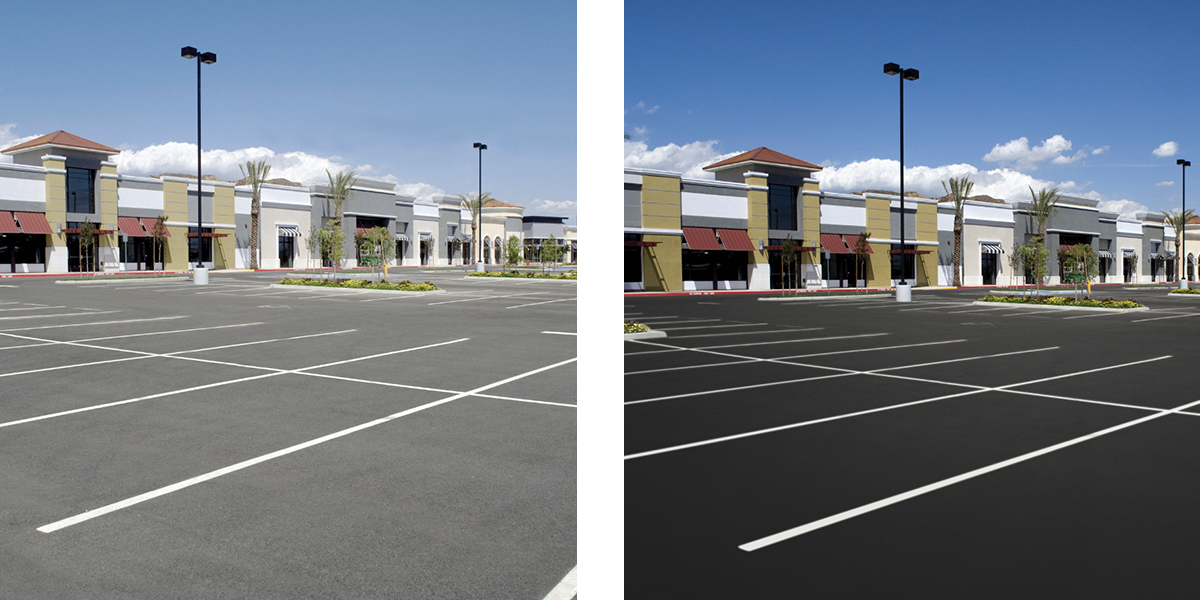
Appearance
- Leaves a uniform, deep black surface
- Improves the curb appeal of driveways, parking lots and roads

Cost savings
- Is a fraction of the cost of repair or replacement
- More than doubles pavement life when part of a regular maintenance program
- Costs only pennies per square foot compared with full pavement replacement
A program of routine sealcoating and crack filling can significantly extend pavement service life.
Why Asphalt-Based Sealer Is the Future
SealMaster has produced asphalt-based sealer in the western United States since the 1970s, building a reputation that has made SealMaster the No. 1 recognized brand of asphalt pavement sealer. Asphalt-based pavement sealer is a proven alternative to coal tar, offering a balance of performance, safety and environmental responsibility.
Benefits include:
- User-friendly application with no burning
- Low to no odor
- Near-zero PAHs
- Environmentally friendly formulation
- Greater flexibility that resists check cracking
These qualities make asphalt-based sealer a leading choice for modern pavement maintenance.

How Asphalt Sealcoating Protects Pavement
Sealcoating provides a protective barrier that helps shield pavement from the elements.
It helps block:
- Water
- Oils
- UV rays
When applied according to manufacturers’ specifications, asphalt sealcoating also offers a slip-resistant surface and revitalizes pavement with a clean, black finish.
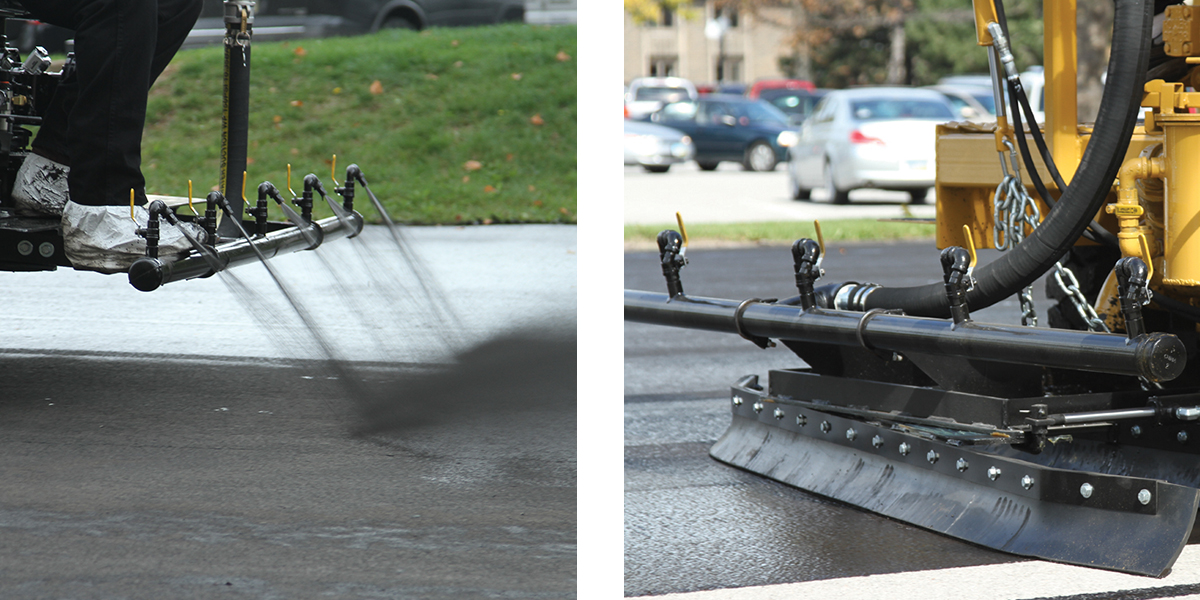
How to Apply Asphalt Sealcoating
To get the best performance from asphalt sealcoating, follow these guidelines:
- Apply a minimum of two coats (squeegee the 1st coat and spray the 2nd for a clean finish)
- Ensure temperatures are at least 50 degrees and rising for 24 hours
- Do not apply if temperatures are forecast to fall below 50 degrees
- Do not apply if rain is expected within 24 hours
- Allow the sealcoat to cure for 24 hours before allowing vehicle traffic
Proper application helps ensure maximum protection.
How Often to Sealcoat Pavement
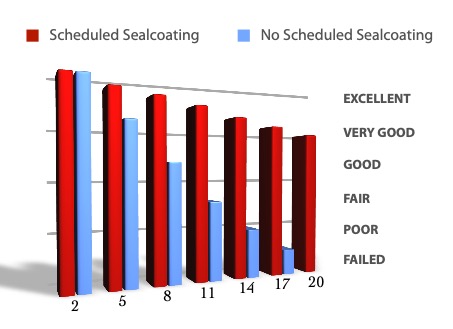
Sealcoating every two to three years helps extend pavement life at minimal cost. When applied at the right time, sealcoating:
- Helps prevent oxidation
- Reduces weather damage
- Beautifies pavement
A consistent maintenance program is the most effective way to protect your investment in asphalt pavement.
Learn More About How to Sealcoat
Sealcoating is most effective when paired with proper surface preparation and routine crack maintenance. To see how these steps come together in the field, explore our hands-on guide, Sealcoat 101: How to Sealcoat Asphalt Pavement. This article walks you through cleaning, repairs, crack filling, application methods and the conditions needed for a durable, professional finish.
Get the full process: Sealcoat 101: How to Sealcoat Asphalt Pavement
SealMaster Expertise and Support
With more than 60 years of industry experience and more than 3 billion gallons of pavement sealer applied worldwide, SealMaster is your one-stop source for all things sealcoating. SealMaster’s national network of professional contractors provides full-service pavement maintenance solutions, including pothole repair, crack filling, sealcoating and much more.
For expert guidance, product recommendations or to connect with a pavement maintenance specialist, contact your local SealMaster for a free inspection or project estimate today.
